Zhang, Y., Kouvaros, P., Lomuscio, A. (2025)
39th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2025)
Outcome Value
Neural network (NN) verification methods provide local robustness guarantees for a NN in the dense perturbation space of an input. A key difficulty with state-of-the-art methods and tools lies in their lack of scalability to large, transformer-based NNs used in present-day applications such as visual transformers and language models. In this paper we introduce H2V, a novel optimization-based method for the validation of NNs that scales to models with hundreds of millions of tuneable parameters thereby enabling the validation of large NNs that were previously out of reach via standard methods.
Summary
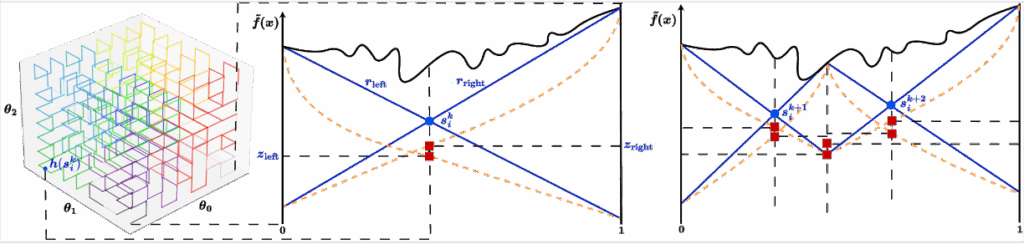
The H2V method as presented targets NN robustness validation against geometric perturbations, such as camera rotation, scaling and translation. It uniquely employs a Hilbert space-filling construction to recast multi-dimensional optimization problems into single-dimensional ones combined withHölder optimization, iteratively refining the estimation of the Hölder constant for constructing the lower bound. In common with other optimization methods, Hölder optimization can theoretically converge to a local minimum, resulting in a potentially incorrect robustness result. However, we have identified conditions under which H2V is provably sound, and shown experimentally that even outside such soundness conditions, the risk of incorrect results can be minimized by introducing appropriate heuristics in the global optimization procedure.
Primary contributions
– We propose H2V as a global optimization method for the validation of neural networks based on spacefilling dimensionality reduction and Hölder optimization. We provide theoretical conditions for theoretical convergence, guaranteeing soundness. We illustrate that when convergence conditions are not met, the potential of a robustness error is well contained. Indeed, no errors were found in the extensive evaluation reported.
– We use H2V to validate the local robustness of models of up to 300M tunable parameters – including ResNet152 and vision transformers for image classification tasks – against geometric properties (rotation, scaling, and translation) on the large-scale ImageNet dataset.
– We use H2V to validate the geometric robustness of 3D ResNet models in video classification tasks for streams of 32 × 3 × 256 × 256 inputs.
What’s next
H2V opens the way for validation of robustness in present-day NNs with hundreds of millions of tuneable parameters including the latest state-of-the-art object detectors of the Yolo family and vision transformers. Future refinements of the methods will include other perturbations beyond geometric transformations, such as photometric changes, blur and beyond.
Link to paper